DEVELOPMENT, IMPROVEMENT AND OPTIMIZATION
New Product Development / Existing Product Improvement
In food business, new product development, modification or product improvement is a systematic process. It might not be as simple and linear as it looks. It outlines the process of bringing altogether a new product to the market or renewing or improving an existing product. It may also include introduction of your existing product to altogether a new market.
New Product, Existing Product or New Market
Nevertheless, if it’s a new product, improvement in the existing product or launching of existing product to a new commercial region. It’s a product transformation. It involves many departments in an organization and is a step-by-step process.

The new product development or existing product improvement must revolve around customer needs and expectations, the nature of the market, business feasibility, and the competitive market environment. In this process., Cost, time and quality are the key variables and essentials.

You are looking to increase your market share, expanding your product range, or planning to overcome a challenge with your existing product, or looking to improve product shelf-life.
It may be a daunting task to do it right first time. There are many bottlenecks, and uncertainties, which a company must face throughout the product development process. Experts at Food Vision suggest some best practices to eliminate or overcome expected challenges in the NPD process.
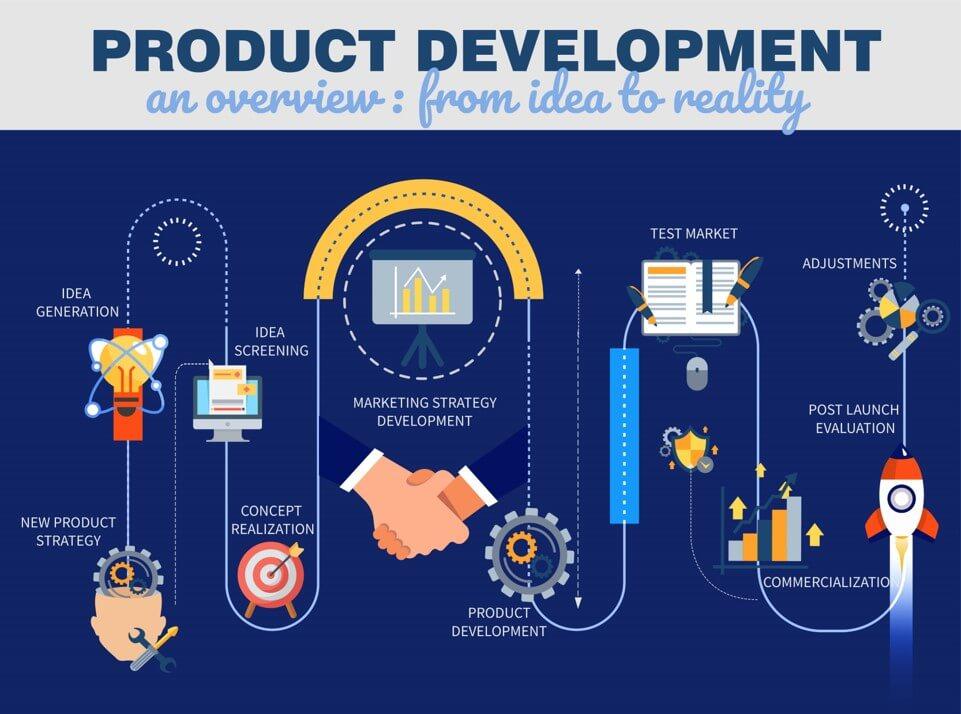
Step by Step Process for New Product Development or Existing Product Improvement
-
New Product Strategy – Having clear objectives and goals.
-
Idea Generation – Having an idea or having brainstorming to find an idea.
-
Idea Screening – Scrutinizing to find the idea that fits to company goal.
-
Concept Development/ Realization – Idea goes through a detailed process to become a reality/ product. Establishing a process to know, how it may be materialized?
-
Market strategy Development Analysis – Cost to Profit analysis. Feasibility Studies and understanding its alignment with the company objectives.
-
Materialization/ Product Development – Developing a proto-type or sample, Materialization and making it ready for the market.
-
Test Market – Run a product trial to the test marketing mix
-
Commercialization – After the successful initial test run, Launch the new product to the market and make it available for the customer/ public.
-
Post Launch Evaluation – Post Launch overview of the performance. Any external research organization may also be involved to monitor the progress of new product and see its compliance to the intended objectives.
-
Make Modification/ Adjustment – Based on the progress, adjustment into the product or strategy may be made to maximise the output

PROCESS IMPROVEMENT, PRODUCT & PROCESS VALIDATION & SYSTEM TROUBLESHOOT

Process and Product Improvement
At times, the product improvement process may not be the only way to improve the product quality and attributes or shelf life. In such scenarios, improvement and modifications in the existing process may be the way to go. At times, after the product has been modified, you might have to optimize the process to get the best results.
Beyond ongoing improvement and process optimization and validation for regulatory compliance, Food Vision has the expertise to offer technical support for ongoing process challenges, failures, and modifications and upgrades.
Diversified reasons for products and process changes and optimization.
- Change of Process
- Changes in Regulation
- Changes in Technology
- Changes in Inputs
- Changes in Customer Requirements
- Advancement in Science and engineering
- Technological advancement – Manual to Automation
- Others
Our areas of service include but not limited to process trouble shoot, re-validation of processes, revalidation of CCPs, Critical Limits and Preventive Controls, shelf life troubleshoot and enhancement, product behavior overview, accelerated shelf life, food packaging migration studies and much more. We have experts to manage product and process behavior for your operations.
To learn more about how our team’s skill and competency can help your cause, click here

Both Safe Food for Canadian Act in Canada and Food Safety Modernization Act in the USA promote the value of preventive controls. Verification and Validation are required by regulatory framework but at times, its confusing or too much for food manufactures to comprehend or challenging to provide right internal resources to meet these regulatory requirements.
PROCESS VALIDATION
Food manufacturers are obligated for developing and implementing a reliable food safety program to control food safety hazards. To ensure processes are not just consistent but also comply with customer requirements, food safety requirements and applicable regulatory requirements, food processes require to verify and validate their processes. Verification ensures process are in place as designed and the Validation ensures processes are not just there, they are doing their job and, are effective.
In some cases, when it matters, these validation strategies must be scientifically valid. The processes may involve compliance to regulatory requirements, i.e., Pasteurization, kill steps, cooking and cooling, pH, water activity, commercial sterility, and others. To see process capability and ensure compliance to stated limits, and achieve certain goals, these studies refer to process validation. Validation entails establishing and supporting the scientific proof that food safety hazards are being effectively and successfully controlled through preventive actions.
The evidence of confirmation may come from diversified sources (Technical and Scientific literature, internal and external reliable historical data, in-house challenge studies, Statistical and mathematical modeling and legal and regulatory frameworks and data bases).
Food Vision’s Technical Resource can make these terms and their application easy for food manufacturers. We have subject experts and process authority to sign-off projects.

PROCESS VALIDATION
- CCP Validation
- Critical Limits Validation
- Sanitation validation
- Allergen Validation
- Environmental Monitoring
- Process Validation
- Lab/ Analytical Validation
- Challenge Studies
- Shelf-Life Validation
- Shelf-Life Studies
- Shelf-Life Enhancement Studies
- Accelerated Shelf Life
- Additive’s behaviour Response
- Packaging Behavior Studies
- Food Packaging – shelf life a market impact analysis
- Consumer Response Studies
- Revalidation Studies
- Recall Response – Revalidation
- Process Optimization studies
- Pre-requisite Program validation
- PCPs Validation
- FSMA – Preventive Controls Validation
- Food Packaging Migration Studies

Role of Process authority
Food regulations in Canada, USA and EU requires low acid canned food products be reviewed by a Process Authority before process are validated and approval is granted. As per the regulations, validation process must be established by a qualified person who has expert knowledge acquired through appropriate training and experience in the “thermal processing requirements for low-acid foods in hermetically sealed containers.
In practice, a processing authority is an individual who has training and expert knowledge of thermal processing requirements for low-acid foods packaged in hermetically sealed containers and/ or has learning and expert knowledge in the acidification and actual processing of acidified foods.
Acidification and low acid foods validation is not the only processes where process authority and validation experts may have a role. Expert opinion may be required in any regulatory compliant thermal process that ensures an adequate kill step (i.e., baking, frying, roasting, cooking, smoking and others). Based on the nature of operation and level of automation, the challenges may be bigger and overall validation may be complex. There are so many variables in process validation. Process validation requires to evaluate the worse scenario to optimize equipment and process parameters. In thermal process validation, the cold spots may be a question, heat exposure time, temperature variation and drift over time and the run time could be an issue. The process authority accounts for all these challenges and finally come up with the right strategy for high-risk food operations.
GFSI -Schemes (SQF, BRC, IFS, FSSC 22000, others) Verification and Validation Requirements


All GFSI benchmarked food safety standards and schemes (SQF, BRC, IFS, FSSC 22000, others) require verification and validation of critical limits, CCPs and pre-requisites.
Based on feedback from our consulting and auditing group, establishing verification and validation under these GFSI benchmarked schemes may be confusing and tricky and be a daunting task for professionals and companies.
We know how to do it, and our consultation may crease ease for your operation.
Food Vision experts can review your existing program, write, or modify program as needed, train your internal validation team, share implementation strategies, help in designing and implementation strategies, work with the labs to coordinate, and last but not the least can communicate with your customers and interact with regulatory authorities on your behalf to make your process and project a success.






